Setup & Options¶
You can configure your synchronization model with some parameters, available through the SyncSetup and SyncOptions objects :
What’s the differences between SyncSetup and SyncOptions ?
SyncSetupcontains all the parameters related to your schema, and shared between the server and all the clients.- In Http mode, the
SyncSetupparameters are set by the Server and will be send to all Clients.
- In Http mode, the
SyncOptionscontains all the parameters not shared between the server and all the clients.
SyncSetup¶
If we look at the SyncSetup object, we mainly have properties about your synced tables schema:
public class SyncSetup
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the scope name
/// </summary>
public string ScopeName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets all the synced tables
/// </summary>
public SetupTables Tables { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Specify all filters for each table
/// </summary>
public SetupFilters Filters { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Specify a prefix for naming stored procedure. Default is empty string
/// </summary>
public string StoredProceduresPrefix { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Specify a suffix for naming stored procedures. Default is empty string
/// </summary>
public string StoredProceduresSuffix { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Specify a prefix for naming stored procedure. Default is empty string
/// </summary>
public string TriggersPrefix { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Specify a suffix for naming stored procedures. Default is empty string
/// </summary>
public string TriggersSuffix { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Specify a prefix for naming tracking tables. Default is empty string
/// </summary>
public string TrackingTablesPrefix { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Specify a suffix for naming tracking tables.
/// </summary>
public string TrackingTablesSuffix { get; set; }
}
The SynchronizeAsync() method creates a SyncSetup instance automatically when called.
For instance, these two instructions are equivalent:
var tables = new string[] {"ProductCategory", "ProductModel", "Product",
"Address", "Customer", "CustomerAddress", "SalesOrderHeader", "SalesOrderDetail" };
var agent = new SyncAgent(clientProvider, serverProvider);
var r = await agent.SynchronizeAsync(tables);
var setup = new SyncSetup("ProductCategory", "ProductModel", "Product",
"Address", "Customer", "CustomerAddress", "SalesOrderHeader", "SalesOrderDetail");
var agent = new SyncAgent(clientProvider, serverProvider);
var r = await agent.SynchronizeAsync(setup);
The main advantage of using SyncSetup is you can personalize what you want from your database:
Schema¶
Note
The schema feature is only avaialable for SQL Server
One great feature in SQL Server is the schema option.
You can configure your sync tables with schema if you target the SqlSyncProvider.
You have two way to configure schemas:
- Directly during the tables declaration, as string.
var tables = new string[] { "SalesLT.ProductCategory", "SalesLT.ProductModel", "SalesLT.Product",
"Address", "Customer", "CustomerAddress"};
- On each table, from the
SyncSetupsetup instance.
var setup = new SyncSetup ("ProductCategory", "ProductModel", "Product",
"Address", "Customer", "CustomerAddress");
setup.Tables["ProductCategory"].SchemaName = "SalesLt";
setup.Tables["ProductModel"].SchemaName = "SalesLt";
setup.Tables["Product"].SchemaName = "SalesLt";
Warning
Schemas are not replicated if you target SqliteSyncProvider or MySqlSyncProvider as client providers.
Filtering Columns¶
Once your SyncSetup instance is created (with your tables list), you can specify the columns you want to sync:
var setup = new SyncSetup("ProductCategory", "ProductModel", "Product",
"Address", "Customer", "CustomerAddress", "SalesOrderHeader", "SalesOrderDetail" );
// Filter columns
setup.Tables["Customer"].Columns.AddRange(new string[] {
"CustomerID", "EmployeeID", "NameStyle", "FirstName", "LastName" });
setup.Tables["Address"].Columns.AddRange(new string[] {
"AddressID", "AddressLine1", "City", "PostalCode" });
For instance, table Customer and Address won’t sync all their columns, but only those specified.
Filtering Rows¶
From your SyncSetup instance, you can also specify a SetupFilter on each table, allowing you to filter rows.
setup.Filters.Add("Customer", "CustomerID");
setup.Filters.Add("CustomerAddress", "CustomerID");
setup.Filters.Add("SalesOrderHeader", "CustomerID", "SalesLT");
Tables Customer, CustomerAddress and SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader will filter their rows, based on the CustomerID column value.
Note
Filtering rows is a quite complex thing. A full chapter is dedicated to rows filtering: Filters
Database configuration¶
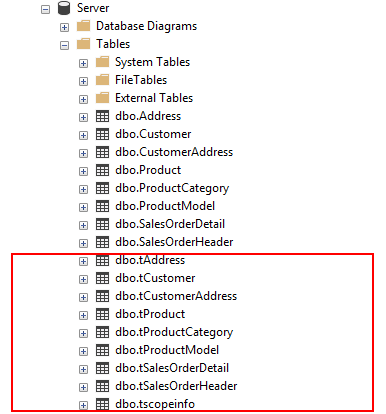
You can personalize how are created the tracking tables, triggers and stored procedures tables in your database:
var setup = new SyncSetup(tables)
{
StoredProceduresPrefix = "s",
StoredProceduresSuffix = "",
TrackingTablesPrefix = "t",
TrackingTablesSuffix = "",
TriggersPrefix = "",
TriggersSuffix = "t"
};
HTTP mode¶
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
services.AddDistributedMemoryCache();
services.AddSession(options => options.IdleTimeout = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(30));
// Get a connection string for your server data source
var connectionString = Configuration.GetSection("ConnectionStrings")["DefaultConnection"];
// Create the setup used for your sync process
var tables = new string[] {"ProductCategory",
"ProductDescription", "ProductModel",
"Product", "ProductModelProductDescription",
"Address", "Customer", "CustomerAddress",
"SalesOrderHeader", "SalesOrderDetail" };
var setup = new SyncSetup(tables)
{
StoredProceduresPrefix = "s",
StoredProceduresSuffix = "",
TrackingTablesPrefix = "t",
TrackingTablesSuffix = "",
TriggersPrefix = "",
TriggersSuffix = "t"
};
// add a SqlSyncProvider acting as the server hub
services.AddSyncServer<SqlSyncProvider>(connectionString, setup);
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseSession();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => endpoints.MapControllers());
}
Warning
The prefix and suffix properties, are not shared betweeen server and client.
SyncOptions¶
SyncOptions can be customized on server and on client, with their own different values.BatchDirectory (representing the tmp directory when batch is enabled) on server and on client./// <summary>
/// This class determines all the options you can set on Client & Server,
/// that could potentially be different
/// </summary>
public class SyncOptions
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the directory used for batch mode.
/// Default value is [User Temp Path]/[DotmimSync]
/// </summary>
public string BatchDirectory { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the directory where snapshots are stored.
/// This value could be overwritten by server is used in an http mode
/// </summary>
public string SnapshotsDirectory { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the size used (approximatively in kb, depending on the serializer)
/// for each batch file, in batch mode.
/// Default is 0 (no batch mode)
/// </summary>
public int BatchSize { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the log level for sync operations. Default value is false.
/// </summary>
public bool UseVerboseErrors { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets if we should use the bulk operations. Default is true.
/// If provider does not support bulk operations, this option is overrided to false.
/// </summary>
public bool UseBulkOperations { get; set; } = true;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets if we should clean tracking table metadatas.
/// </summary>
public bool CleanMetadatas { get; set; } = true;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets if we should cleaning tmp dir files after sync.
/// </summary>
public bool CleanFolder { get; set; } = true;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets if we should disable constraints before making apply changes
/// Default value is true
/// </summary>
public bool DisableConstraintsOnApplyChanges { get; set; } = true;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the scope_info table name. Default is scope_info
/// On the server side, server scope table is prefixed with _server
/// and history table with _history
/// </summary>
public string ScopeInfoTableName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the default conflict resolution policy. This value could potentially
/// be ovewritten and replaced by the server
/// </summary>
public ConflictResolutionPolicy ConflictResolutionPolicy { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or Sets the default logger used for logging purpose
/// </summary>
public ILogger Logger { get; set; }
}
Note
If nothing is supplied when creating a new SyncAgent instance, a default SyncOptions is created with default values.
SyncOptions has some useful methods, you can rely on:
/// <summary>
/// Get the default Batch directory full path ([User Temp Path]/[DotmimSync])
/// </summary>
public static string GetDefaultUserBatchDiretory()
/// <summary>
/// Get the default user tmp folder
/// </summary>
public static string GetDefaultUserTempPath()
/// <summary>
/// Get the default sync tmp folder name (usually 'DotmimSync')
/// </summary>
public static string GetDefaultUserBatchDirectoryName()
Batch mode¶
Batch mode is an important options if you have to deal with over sized sync changes.
The BatchSize property from the SyncOptions object allows you to define the maximum size of any payload:
var clientOptions = new SyncOptions { BatchSize = 500 };
Warning
BatchSize value regarding your result and expectation.Example
Hint
You will find the complete sample here : Batch size sample
As an example, we make an insert of 100000 product category items in the server database, before making our sync:
Insert into ProductCategory (Name)
Select SUBSTRING(CONVERT(varchar(255), NEWID()), 0, 7)
Go 100000
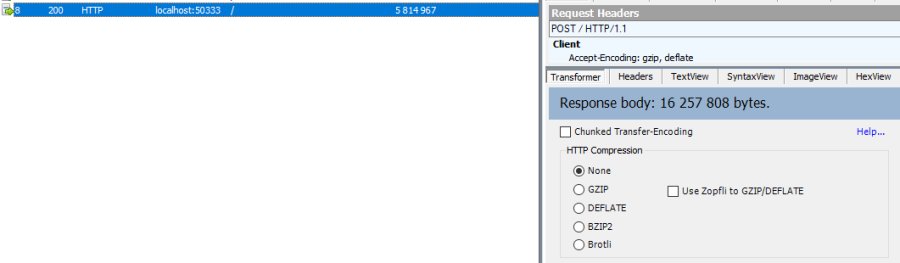
By default, here is a sync process, where we download everything from the server, without any BatchSize option:
var agent = new SyncAgent(clientProvider, proxyClientProvider);
await agent.SynchronizeAsync(setup);
Here is the fiddler trace:
Here is the same sync, with the batch mode enabled:
// ----------------------------------
// Client side
// ----------------------------------
var clientOptions = new SyncOptions { BatchSize = 500 };
var agent = new SyncAgent(clientProvider, proxyClientProvider, clientOptions);
var progress = new SynchronousProgress<ProgressArgs>(pa =>
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0} -{1}\t {2}",
pa.Context.SessionId, pa.Context.SyncStage, pa.Message));
var s = await agent.SynchronizeAsync(progress);
Console.WriteLine(s);
Hint
The client side dictates the batch size. The server is always adapting its payload, regarding the client ask.
Here is the fiddler trace:
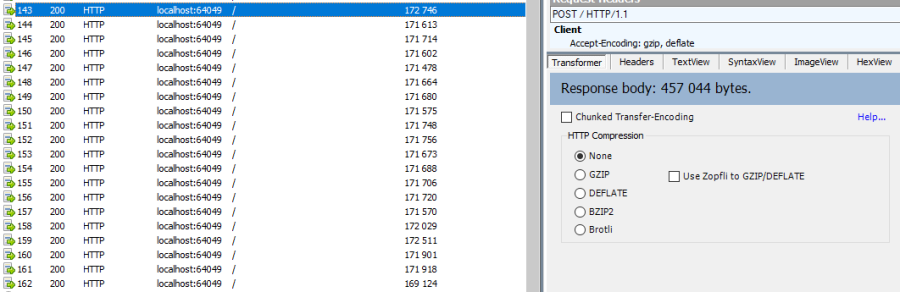
And the progress of the sync process:
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - BeginSession 10:53:38.762 Session Id:974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ScopeLoaded 10:53:39.385 [Client] [DefaultScope] [Version ] Last sync: Last sync duration:0:0:0.0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - Provisioned 10:53:42.224 [Client] tables count:8 provision:Table, TrackingTable, StoredProcedures, Triggers
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesSelected 10:53:42.243 [Client] upserts:0 deletes:0 total:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:55.133 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:5171 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:55.702 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:10343 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:56.297 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:15515 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:56.891 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:20687 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:57.620 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:25859 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:58.280 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:31031 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:58.971 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:36203 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:53:59.682 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:41375 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:00.420 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:46547 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:01.169 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:51719 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:01.940 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:56891 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:02.657 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:62063 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:03.432 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:67235 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:04.192 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:72407 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:05.82 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:77579 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:05.930 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:82751 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:06.787 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:87923 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:07.672 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:93095 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:08.553 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:98267 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:08.972 [Client] [ProductCategory] Modified applied:100041 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.113 [Client] [ProductModel] Modified applied:128 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.183 [Client] [Product] Modified applied:198 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.208 [Client] [Product] Modified applied:295 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.255 [Client] [Address] Modified applied:450 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.329 [Client] [Customer] Modified applied:847 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.375 [Client] [CustomerAddress] Modified applied:417 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.414 [Client] [SalesOrderHeader] Modified applied:32 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplying 10:54:09.476 [Client] [SalesOrderDetail] Modified applied:542 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - ChangesApplied 10:54:09.636 [Client] applied:102752 resolved conflicts:0
974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7 - EndSession 10:54:09.638 Session Id:974f8be9-332d-4d6d-b881-7784b63b4bb7
Synchronization done.
Total changes uploaded: 0
Total changes downloaded: 102752
Total changes applied: 102752
Total resolved conflicts: 0
Total duration :0:0:30.886
As you can see, most of the product category items come from different batch requests.
UseBulkOperations¶
This option is only available when using SQL Server providers.
It allows you to use bulk operations from within SQL Server using Table Value Parameters as input to the stored procedures.
When using UseBulkOperations, each table will have new stored procedures and one table value parameter:
- Stored procedure
CustomerAddress_bulkdelete - Stored procedure
CustomerAddress_bulkupdate - Table value parameter
Customer_BulkType
Using this option will increase your performances, so do not hesitate to use it !
CleanMetadatas¶
The CleanMetadatas option allows you to clean the _tracking tables from your client databases.
Once enabled, the client database will delete all metadatas from the tracking tables, after every successful sync.
Be careful, the delete method will:
- Work only if client download something from server. If there is no changes downloaded and applied on the client,
DeleteMetadasAsyncis not called - Work only on T-2 metadatas. To be more secure, the T-1 values stays in the tracking tables.
You can also manually delete metadatas from both server or client, using the method DeleteMetadatasAsync, available from both LocalOrchestrator and RemoteOrchestrator:
var clientProvider = new SqlSyncProvider(DbHelper.GetDatabaseConnectionString(clientDbName));
var localOrchestrator = new LocalOrchestrator(clientProvider);
await localOrchestrator.DeleteMetadatasAsync();
Note
If you’re using SqlSyncChangeTrackingProvider, the metadatas cleansing is automatically handled by the change tracking feature.
DisableConstraintsOnApplyChanges¶
The DisableConstraintsOnApplyChanges will disable all constraint on your database, before the sync process is launched, and will be enabled after.
Use it if you’re not sure of the table orders.
ScopeInfoTableName¶
This option allows you to customize the scope info table name. Default is scope_info.
On the server side, server scope table is prefixed with _server and history table with _history